Ceramic PCB Manufacturing
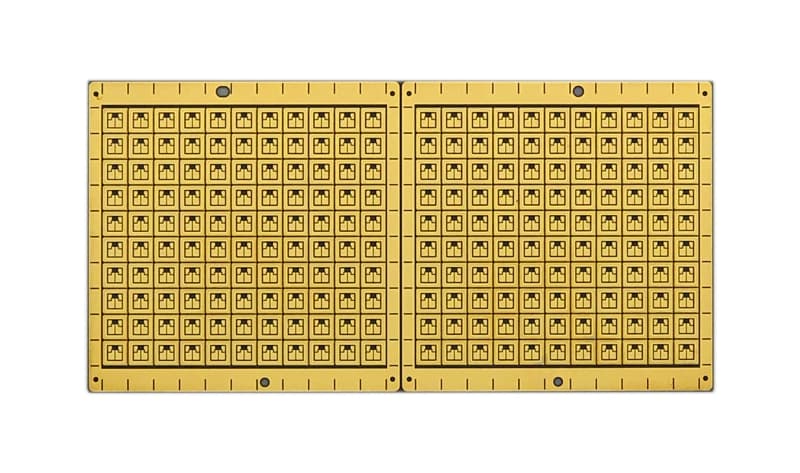
What is Ceramic PCB
With the advancement of electronic technology, there is an increasing demand for highly integrated circuit boards. These boards require an efficient heat dissipation system and low coefficient of thermal expansion.
Ceramic PCBs are organic ceramic circuit boards designed to provide excellent thermal conductivity, typically ranging from 9 to 20W/ M.K. Ceramic substrates can achieve a thermal conductivity of around 220W/M. K, providing significantly enhanced heat dissipation capabilities.
Types of Ceramic PCBs
There are several types of ceramic PCBs categorized based on their materials, including alumina PCBs, aluminum nitride ceramic PCBs, silicon nitride PCBs, and silicon carbide PCBs.
Alumina PCB
Aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) PCB, also known as alumina PCB, holds a prominent position in the current market due to its cost-effectiveness and favorable properties. Alumina boasts excellent thermal conductivity and electrical resistance, obviating the need for an additional insulation layer when using alumina PCBs.Within the alumina PCB market, you’ll come across 75%, 96%, and 99% alumina PCBs. Higher purity levels correspond to better properties but also entail higher costs.Alumina PCBs primarily find their application in LEDs with power ratings ranging from 3W to 5W.
Aluminum Nitride PCB
Aluminum nitride PCBs are widely regarded as the future’s most promising ceramic PCBs. Applications for AlN PCBs include high-power LEDs, power modules, and various fields in laser technology. They excel at rapidly dissipating heat from ICs and other valuable components.
Another compelling reason for the popularity of AlN PCBs in high-power LEDs and power modules is their closely matched thermal expansion coefficient of 4.6×10ˆ-6°C with semiconductors like Si (3.5~4×10ˆ-6°C). Since these high-power devices use Si for their chips, the similar thermal expansion coefficients ensure that the chips remain securely attached to the AlN PCB base plate, even during thermal deformation.
Silicon Nitride PCB
In contrast to traditional and fragile ceramic materials, silicon nitride PCBs, often referred to as Si₃N₄ PCBs, exhibit remarkable mechanical strength and fracture toughness even under high temperatures. Furthermore, Si₃N₄ PCBs boast exceptional thermal conductivity, measuring at 80+W/mK. Additionally, they possess a thermal expansion coefficient that aligns perfectly with silicon (Si).It’s for these reasons that silicon nitride PCBs are the material of choice for vehicle-class modules. These vehicle modules also operate in environments characterized by vibrations, making impact resistance a crucial factor for safety.
Silicon Carbide PCB
Silicon carbide (SiC) is essentially a form of diamond, differing only in terms of carbon ratios. As a result, SiC PCBs exhibit an extraordinarily high level of thermal resistance, making them capable of functioning effortlessly at temperatures as high as 1000°C. This exceptional thermal resilience renders them suitable for applications in laser technology. It’s important to note that the manufacturing process for SiC PCBs is currently prohibitively expensive.
Searching Ceramic PCBs Supplier?
Our team of experts stands ready to assist you in acquiring the finest ceramic PCBs for your specific product requirements. By partnering with us, you can rest assured that our dedicated staff is not only attuned to your needs but also possesses the requisite expertise to consistently deliver top-tier, high-quality outcomes.
Advantages of Ceramic PCB
Ceramic PCBs offer several advantages compared to traditional PCB substrates made of materials like epoxy resin and fiberglass. Here are some key points to summarize the advantages of ceramic PCB:
High Temperature Resistance
Ceramic PCBs are capable of withstanding high temperatures without losing their structural integrity. Unlike ordinary PCB boards that have low ignition points and limited heat resistance, ceramic substrates can handle elevated temperatures, making them suitable for applications where thermal management is critical.
Excellent Thermal Conductivity
Ceramic substrates have high thermal conductivity, allowing efficient dissipation of heat generated by electronic components. For example, the thermal conductivity of aluminum nitride ceramic boards can be as high as 170-230W/MK, while ordinary PCB substrates typically have a thermal conductivity of 1.0W/MK.
Chemical Stability and Corrosion Resistance
Ceramic PCBs are chemically stable and resistant to corrosion. They can withstand exposure to corrosive environments and prolonged immersion, making them suitable for electronic products that require resistance to chemicals or liquids.
Insulating Properties
Ceramic substrates are inherently insulating materials, eliminating the need for additional insulation layers in the PCB design. This simplifies the manufacturing process and reduces the overall complexity of the PCB.
Strong Bonding with Metal Layers
Ceramic substrates exhibit strong bonding capabilities with metal layers, such as titanium and copper. The thermal expansion coefficients of ceramic and metal are often well-matched, allowing for a firm and reliable bond even under high-temperature conditions. This ensures the stability and durability of the PCB.
High Mechanical Hardness and Low Dielectric Constant
Ceramic substrates possess high mechanical hardness and low dielectric constants. These properties make them suitable for applications in the high-frequency range, where signal loss rates can be significantly reduced compared to traditional PCB materials.
Electrical Safety
Ceramic PCBs have a high breakdown voltage, ensuring the safe operation of electronic equipment, especially in the presence of sudden high voltages. This characteristic contributes to the overall safety of the PCB and the protection of both the equipment and the operator.
Processes of Ceramic PCB
The copper clad process of ceramic copper-clad laminates and the thick film process of ceramic PCB are two different methods of applying copper layers to ceramic substrates. Here’s a comparison of these two processes:
Thin Film Circuit Process
The initial step in the thin film circuit process involves creating ultra-fine circuit patterns on the ceramic substrate, and there are several methods to achieve this:
- Magnetron Sputtering: One option is to use magnetron sputtering.
- Pattern Lithography: Pattern lithography is another technique to consider.
- Dry Wet Etching: Dry wet etching can also be employed.
- Electroplating Thickening: Thickening can be accomplished through electroplating.
Thick Film Circuit Process
There are various thick film circuit processes available, including high-temperature co-fired ceramic, low-temperature co-fired ceramic, and direct bonded copper. The following steps are involved:
- Drilling: Mechanically drill holes on the board to create connecting pipes between metal layers.
- Plated Through Hole: After drilling holes between the copper layers, create connecting paths.
- Dry Film Pressing: Apply a photosensitive layer.
- Inner Layer Image Transfer: Use exposure to transfer the image of the film onto the board surface.
- Outer Layer Exposure: Similar to the inner layers, this photo film defines areas of the PCB to be plated and un-plated.
- Magnetron Sputtering: This process transfers material from the source to the substrate to achieve film deposition.
- Etching – Formation of External Lines: This step is crucial for ceramic board fabrication, removing unwanted materials through chemical reactions.
- Anti-Weld Coating: Ceramic circuit boards primarily serve to carry electronic components and facilitate connections. After completing the circuit board, define the placement of electronic and non-electronic components. Protect the no-assembly area with polymer material.
Choose Highleap as Your PCB Manufacturer

Full Expertise
We have rich experience in all kinds of PCB manufacturing and assembly.From component procurement to product delivery, we can complete every step with high quality.
Strong Supplier Network
With 10 years of experience in the PCB industry, Highleap owns a supplier network that provides us with reliable access to get high-quality components at competitive prices.

Strict Quality Control
At each process, we strictly control the quality by implementing a variety of testing and inspections to ensure that each PCBA reaches the highest quality standard.
Take a Quick Quote
Discover how our expertise can help with your next PCB project.
