IPC Standard
Guide to IPC Standards for PCB Design, Manufacturing and Assembly
What is IPC standard
IPC standards are a series of industry standards developed and published by IPC (the Association Connecting Electronics Industries). They aim to standardize various aspects of electronic product design, manufacturing, and assembly. IPC standards cover multiple domains within the electronics industry, including electronic assembly, printed circuit board (PCB) design and manufacturing, soldering, testing, and quality control, among others.Learn about industry-adopted IPC standards governing the design, assembly, inspection, testing, and documentation of printed circuit boards (PCBs).
The development of IPC standards is based on the input and expertise of industry experts and undergoes extensive industry discussions and reviews. These standards are designed to provide a common language and guidance to ensure consistency and quality throughout the design, manufacturing, and assembly processes of electronic products.
IPC standards encompass many critical aspects, such as PCB design specifications, component placement and soldering standards, wiring and interconnection specifications, surface mount technology, testing methods, and standards, among others. These standards provide detailed descriptions of best practices and requirements at each stage to ensure the functionality, reliability, and manufacturability of electronic products.
The application of IPC standards is highly significant in the electronics industry. They facilitate communication and collaboration among manufacturers, designers, engineers, and suppliers, ensuring that they follow common standards and processes. By using IPC standards, the electronics industry can enhance product quality, reduce manufacturing costs, improve production efficiency, and ensure compliance with international quality and safety standards.
In addition to developing standards, IPC also offers training and certification programs to help professionals understand and apply IPC standards. These training programs cover knowledge and skills in various areas, such as PCB design, soldering techniques, quality control, and reliability engineering.
In summary, IPC standards play a crucial role in the electronics industry. They provide a set of common standards and guidelines to ensure consistency and quality throughout the design, manufacturing, and assembly of electronic products, fostering industry development and innovation. By adhering to IPC standards, businesses can enhance product quality, ensure compliance, and gain a competitive edge in the global market.IPC standards are the electronics-industry-adopted standards for design, PCB manufacturing, and electronic assembly. There’s an IPC standard associated with just about every PCB design, production, and assembly .
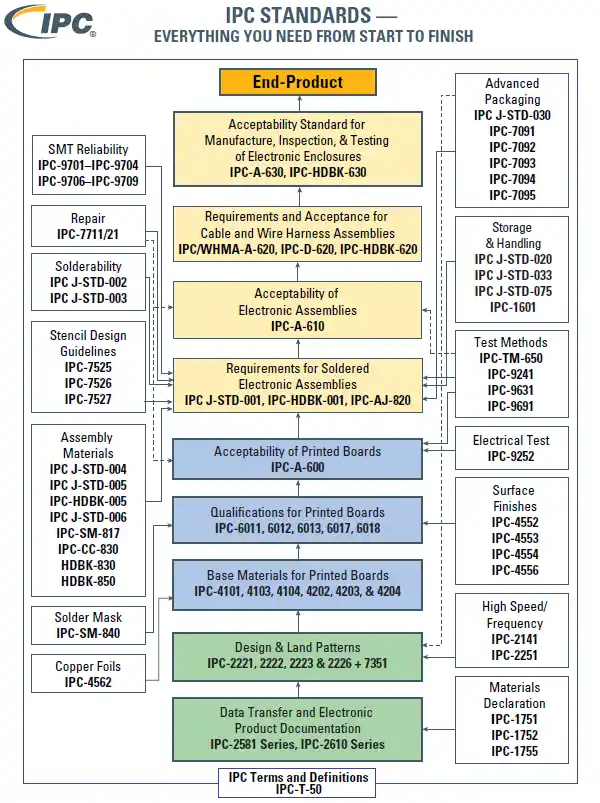
IPC standard--Source:ipc.org
IPC standards play a crucial role in the electronics industry. They provide a set of common standards and guidelines to ensure consistency and quality throughout the design, manufacturing, and assembly of electronic products, fostering industry development and innovation. By adhering to IPC standards, businesses can enhance product quality, ensure compliance, and gain a competitive edge in the global market.
The Importance of IPC Standards
IPC standards are highly significant in the electronics industry for several reasons:
1. Consistency and Quality
IPC standards establish a common set of guidelines and best practices that ensure consistency and quality throughout the design, manufacturing, and assembly processes of electronic products. By following these standards, companies can achieve higher levels of product reliability, functionality, and performance.
2. Industry Alignment
IPC standards help align industry practices and processes, serving as a universal language that facilitates communication and collaboration among manufacturers, designers, engineers, and suppliers. This alignment promotes efficiency, interoperability, and overall industry advancement.
3. Risk Mitigation
Adhering to IPC standards helps mitigate risks associated with product failures, safety hazards, and non-compliance. By following established guidelines, companies can identify and address potential issues early in the product life cycle, ensuring products meet safety requirements and minimizing the possibility of costly recalls or legal consequences.
4. Cost Efficiency
IPC standards contribute to cost efficiency by optimizing design, manufacturing, and assembly processes. They provide guidelines for material selection, layout, and production techniques that help reduce waste, optimize resource utilization, and streamline operations, leading to cost savings and improved profitability.
5. Customer Confidence
Compliance with IPC standards enhances customer confidence and trust in electronic products. Customers rely on these standards as a benchmark for product quality, safety, and reliability. By adhering to IPC standards, companies demonstrate their commitment to meeting customer expectations and delivering high-quality, compliant products.
6. Regulatory Compliance
IPC standards often align with regulatory requirements and industry certifications. Compliance with these standards helps companies ensure adherence to relevant regulations, such as safety, environmental, and quality standards. It streamlines the certification process and facilitates market access, both domestically and internationally.
7. Continuous Improvement
IPC standards are regularly updated to address emerging technologies, industry trends, and customer needs. By staying informed and adopting the latest standards, companies can embrace technological advancements, improve processes, and remain competitive in a dynamic and evolving industry.
In summary, IPC standards play a vital role in ensuring consistency, quality, risk mitigation, cost efficiency, customer confidence, regulatory compliance, and continuous improvement in the electronics industry. They serve as a cornerstone for excellence, innovation, and the delivery of safe and reliable electronic products.
Standards published by IPC
IPC standards are widely utilized within the electronics manufacturing industry. One such prominent standard is IPC-A-610, known as the “Acceptability of Electronic Assemblies,” which enjoys global adoption by original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and Electronics Manufacturing Services (EMS) companies. Across the globe, more than 3,600 certified trainers are equipped to provide training and assessment based on this standard. The development of these standards is the result of collaborative efforts from committees comprised of dedicated industry volunteers. Notably, task groups have been established in China, the United States, and Denmark to further advance these standards.Here is an overview of some key IPC standards:
General Documents
- IPC-T-50 Terms and Definitions
- IPC-2615 Printed Board Dimensions and Tolerances
- IPC-D-325 Documentation Requirements for Printed Boards
- IPC-A-31 Flexible Raw Material Test Pattern
- IPC-ET-652 Guidelines and Requirements for Electrical Testing of Unpopulated Printed Boards
Design Specifications
- IPC-2612 Sectional Requirements for Electronic Diagramming Documentation (Schematic and Logic Descriptions)
- IPC-2141A Design Guide for High-Speed Controlled Impedance Circuit Boards
- IPC-2221 Generic Standard on Printed Board Design
- IPC-2223 Sectional Design Standard for Flexible Printed Boards
- IPC-2251 Design Guide for the Packaging of High Speed Electronic Circuit
- IPC-7351B Generic Requirements for Surface Mount Design and Land Pattern Standards
Material Specifications
- IPC-FC-234 Pressure Sensitive Adhesives Assembly Guidelines for Single-Sided and Double-Sided Flexible Printed Circuits
- IPC-4562 Metal Foil for Printed Wiring Applications
- IPC-4101 Laminate Prepreg Materials Standard for Printed Boards
- IPC-4202 Flexible Base Dielectrics for Use in Flexible Printed Circuitry
- IPC-4203 Adhesive Coated Dielectric Films for Use as Cover Sheets for Flexible Printed Circuitry and Flexible Adhesive Bonding Films
- IPC-4204 Flexible Metal-Clad Dielectrics for Use in Fabrication of Flexible Printed Circuitry
Performance and Inspection Documents
- IPC-A-600 Acceptability of Printed Boards
- IPC-A-610 Acceptability of Electronic Assemblies
- IPC-6011 Generic Performance Specification for Printed Boards
- IPC-6012 Qualification and Performance Specification for Rigid Printed Boards
- IPC-6013 Specification for Printed Wiring, Flexible and Rigid-Flex
- IPC-6018 Qualification and Performance Specification for High Frequency (Microwave) Printed Boards
- IPC- 6202 IPC/JPCA Performance Guide Manual for Single- and Double-Sided Flexible Printed Wiring Boards
PAS-62123 Performance Guide Manual for Single & Double Sided Flexible Printed Wiring Boards - IPC-TF-870 Qualification and Performance of Polymer Thick Film Printed Boards
Flex assembly and materials standards
- IPC-FA-251 Assembly Guidelines for Single and Double Sided Flexible Printed Circuits
- IPC-3406 Guidelines for Electrically Conductive Surface Mount Adhesives
- IPC-3408 General Requirements for Anisotropically Conductive Adhesives Films
Advantages of using IPC standards
- Design Consistency: IPC standards provide clear guidelines and specifications for PCB design, layout, and component placement. By following these standards, companies can achieve design consistency across different projects and ensure compatibility, manufacturability, and reliability of their products.
- Manufacturing Efficiency: IPC standards define best practices for manufacturing processes such as soldering, assembly, and inspection. Adhering to these standards improves manufacturing efficiency, reduces defects, and minimizes rework or scrap. This leads to increased productivity, cost savings, and shorter production cycles.
- Quality Assurance: IPC standards promote quality assurance throughout the production process. By following standardized procedures and specifications, companies can maintain consistent quality levels, identify potential issues early, and implement effective quality control measures. This results in higher product reliability, customer satisfaction, and reduced warranty claims.
- Supply Chain Collaboration: IPC standards facilitate effective collaboration among different stakeholders in the supply chain. Manufacturers, suppliers, and customers can rely on these standards as a common reference point, ensuring clear communication, understanding, and alignment of expectations. This collaboration leads to smoother operations, reduced errors, and improved overall efficiency.
- Compliance and Market Access: IPC standards often align with regulatory requirements and industry certifications. Adhering to these standards helps companies ensure compliance with relevant regulations, demonstrate product safety and reliability, and obtain necessary certifications. This facilitates market access, both domestically and internationally, opening up opportunities for business growth and expansion.
- Continuous Improvement: Highleap keeps pace with industry advancements by staying informed about and implementing the latest IPC standards. This proactive approach allows the company to continuously improve its processes, adopt innovative techniques, and maintain competitiveness in a rapidly evolving industry.
-
Industry Recognition and Reputation: Highleap’s commitment to IPC standards enhances its reputation within the electronics industry. This commitment serves as a testament to the company’s dedication to quality, reliability, and professionalism. Highleap’s customers and partners recognize the value of adhering to these standards, resulting in increased trust, credibility, and potential business opportunities.
In conclusion, Highleap’s integration of IPC standards into its operations yields significant advantages, including design consistency, manufacturing efficiency, quality assurance, supply chain collaboration, compliance and market access, continuous improvement, and enhanced industry recognition. These benefits collectively contribute to improved product quality, heightened customer satisfaction, enhanced operational efficiency, and overall business success within the electronics industry.
The effect of IPC standards
IPC standards are executed for several compelling reasons, underscoring their importance in the electronics manufacturing industry:
Quality Control and Reliability
IPC standards are crafted with extensive input from industry experts and practitioners, involving tens of thousands of professionals. This collective expertise ensures that IPC standards are highly authoritative and reliable. Manufacturers use these standards to exercise rigorous quality control, thereby enhancing the reliability and durability of their final products. This is particularly critical in industries where product failures can have serious consequences.
Global Common Language
IPC standards have created a common language and framework that the entire global electronics industry can adopt and adhere to. This standardization acts as a bridge that connects upstream suppliers with downstream customers. It ensures that all stakeholders can communicate effectively, understand each other’s requirements, and work together seamlessly. This global alignment leads to increased production efficiency and streamlined operations.
Cost Reduction
IPC standards provide clear guidelines and best practices for various manufacturing processes. When manufacturers adhere to these standards, they are less likely to deviate into non-standard processes that can lead to costly errors and defects. By reducing the occurrence of non-standard processes and their associated costs, companies can achieve significant cost savings, resulting in a more efficient and profitable operation.
Validation and Verification
Every IPC standard undergoes rigorous validation and testing before publication. This process ensures that the standards are not only comprehensive but also practical and effective in real-world applications. Manufacturers can trust that these standards have been thoroughly vetted, providing them with confidence in their applicability to their specific processes and products.
In summary, executing IPC standards is an integral part of Highleap’s commitment to delivering high-quality PCB and PCBA solutions. These standards serve as a cornerstone for quality control and reliability, establish a common industry language, boost production efficiency, and lead to cost reductions associated with non-standard processes. Highleap relies on these structured and validated standards to produce top-tier, reliable, and compliant electronic products for our valued clients.
IPC Performance Classes
Highleap, as a PCB & PCBA manufacturer, understands the significance of IPC (Association Connecting Electronics Industries) standards in the electronics manufacturing industry. IPC standards are classified according to the complexity of electronic products, functional performance requirements and frequency of testing/inspection. These classes help define the quality and reliability standards for various electronic products. Here are the IPC performance classes:
IPC Class I – General Electronic Products: This class encompasses consumer products and some computer-related items. It is suitable for applications where cosmetic imperfections are not critical, and the primary requirement is the functional performance of the completed printed board. In Class I, aesthetics are not a primary concern.
IPC Class II – Dedicated Service Electronic Products: Class II includes communication equipment, sophisticated business machines, and instruments where high performance and extended product life are essential. Products in this class are expected to provide uninterrupted service but may tolerate certain cosmetic imperfections. Class II is suitable for applications where cosmetic appearance matters to some extent, but the primary focus remains on functionality and reliability.
IPC Class III – High Reliability or Harsh Operating Environment Electronic Products: Class III is reserved for equipment and products where continuous and reliable performance is absolutely critical. These products are expected to function without downtime and must perform on-demand, especially in scenarios such as life support equipment or flight control systems. Printed boards in Class III are designed for applications that demand a very high level of assurance and where service reliability is paramount.
A-Level or IPC 6012 class 3 – Advanced Electronic Products:IPC 6012 Class 3 signifies the highest PCB quality, crucial for demanding applications like aerospace, military tech, missiles, space equipment, and avionics. These PCBs require strict manufacturing processes, specialized materials, advanced techniques, and thorough quality control, driving up costs. The added expense is justifiable as Class 3 PCBs excel in harsh conditions, delivering unwavering reliability and performance. In summary, these PCBs are designed to meet the most stringent requirements in quality and performance, making them indispensable for critical applications.
It’s important to note that the performance class assigned to a printed board assembly (assembled, soldered, cleaned, and tested) cannot be of a higher class than the one specified for the bare printed board. In other words, if you want a Class 3 recognition for the printed board assembly, the bare printed board must also meet the Class 3 standards. Having a lower class (e.g., Class 2 or Class 1) for the bare printed board will prevent achieving a Class 3 recognition for the printed board assembly. This requirement ensures that the reliability and quality standards of the components and assembly match the intended application and performance level. Highleap adheres to these IPC standards to deliver products that meet the specific quality and reliability requirements of our customers.
IPC Class II VS IPC Class III
IPC II
Advantages of IPC Class II Standards:
- Cost-Effective: IPC Class II standards are cost-effective because they allow for some minor defects and imperfections in electronic assemblies. This means that manufacturers can produce electronics at a lower cost compared to the more stringent Class III standards.
- Faster Production: Because Class II allows for a slightly higher level of imperfections, manufacturers can speed up production processes, leading to quicker turnaround times for electronic products.
- Wider Range of Applications: Class II standards are suitable for a wide range of electronic devices, including consumer electronics, industrial equipment, and many commercial products. This flexibility makes it a versatile choice for manufacturers.
- Lower Inspection Costs: The inspection and quality control requirements for Class II are less stringent compared to Class III. This reduces inspection costs and makes it more accessible for smaller manufacturers.
Disadvantages of IPC Class II Standards:
- Lower Reliability: Class II standards tolerate more defects than Class III, which means that products manufactured under Class II standards may have a slightly lower level of reliability. This can be a concern for critical applications where failure is not an option.
- Limited Suitability for High-Reliability Applications: Class II standards may not be suitable for applications where high reliability is paramount, such as aerospace or medical devices. Manufacturers in these industries typically adhere to the more stringent Class III standards.
- Potential for Inconsistent Quality: With the tolerance for defects, there is a risk of inconsistent quality among products manufactured under Class II standards. This can lead to variability in product performance and customer satisfaction.
- Market Perception: Some customers or industries may prefer or require products manufactured to Class III standards due to their perception of higher quality. Choosing Class II may limit a manufacturer’s market opportunities in such cases.
In summary, IPC Class II standards offer cost-efficiency and flexibility in manufacturing, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. However, they may not be suitable for industries that demand high-reliability products, and there’s a potential trade-off between cost-effectiveness and product quality. Manufacturers must carefully consider the specific requirements of their target market and applications when choosing between IPC Class II and other IPC standards.
IPC III
Advantages of IPC Class III Standards:
- High Reliability: IPC Class III standards demand the highest level of quality and reliability. This makes them ideal for critical applications where product failure is not an option, such as aerospace, medical devices, and military electronics.
- Longevity and Durability: Products manufactured to Class III standards are built to last and withstand extreme conditions. They have a longer operational life and can handle harsh environments.
- Enhanced Quality Control: The strict requirements of Class III standards necessitate rigorous quality control and testing procedures. This results in consistently high-quality products that meet or exceed customer expectations.
- Industry Credibility: Adhering to IPC Class III standards can enhance a company’s reputation and credibility in the industry. It signifies a commitment to excellence and reliability.
Disadvantages of IPC Class III Standards:
- Higher Manufacturing Costs: Meeting the stringent requirements of Class III standards often involves additional manufacturing steps, materials, and testing, all of which can drive up production costs significantly.
- Time-Consuming: The detailed inspections, testing, and documentation required for Class III compliance can extend the production timeline, leading to longer lead times for customers.
- Specialized Expertise: Manufacturers and personnel need specialized training and expertise to meet Class III standards, which can increase labor costs and limit the pool of qualified suppliers.
- Limited Applicability: Class III standards may be considered overkill for some consumer or commercial electronic products where the highest level of reliability is not essential. Using Class III standards for such products can lead to unnecessary expenses.
In summary, IPC Class III standards offer unparalleled reliability and quality, making them essential for industries with stringent requirements. However, they come with higher production costs, longer timelines, and the need for specialized expertise. Therefore, their applicability should be carefully considered based on the specific needs and market demands of a given product or project.
Take a Quick Quote
Discover how our expertise can help with your next PCB project.
