Diode
What is Diode
A diode is a semiconductor device that primarily functions as a one-way switch for current. It allows current to flow in one direction but blocks it in the opposite direction. Diodes are commonly used for rectifying alternating current to direct current (converting AC to DC), in signal demodulation, and as protection devices in various electronic circuits. They consist of a semiconductor material, typically silicon, with two terminals: an anode and a cathode. The unique property of diodes to control the direction of current flow makes them essential components in a wide range of electronic devices.
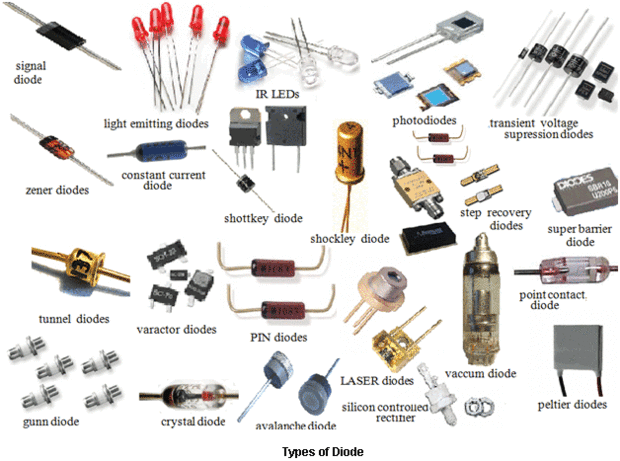
Kinds of Diodes
Here is a comprehensive overview of various types of diodes.
- P-N Junction Diode: A basic type of diode that allows current to flow in the forward direction and blocks it in reverse. It’s typically used for rectification.
- Small Signal Diode: Operates on low voltage signals and is used in high-frequency circuits due to its high switching speed and fast recovery time.
- Rectifier Diode: Commonly used for converting AC into DC, capable of handling heavy current.
- Schottky Diode: Known for its low forward voltage drop and fast switching. It’s used in power rectification and radio frequency applications.
- Super Barrier Diodes (SBR): Combine low forward voltage drop and low reverse leakage current. They are used in rectifier applications and are similar to Schottky diodes but with enhanced characteristics.
- Light Emitting Diode (LED): Converts electrical energy into light energy. LEDs are used in a wide range of applications, from indicator lights to display screens.
- Photodiode: Converts light into electrical current, used in solar cells and light sensors.
- Laser Diode: Produces coherent light and is used in optical communication and various electronic devices like CD drives.
- Tunnel Diode: Known for its negative resistance region, used in oscillators and microwave amplifiers.
- Zener Diode: Used for voltage regulation in reverse bias configuration, providing a stabilized voltage.
- Backward Diode: Operates similarly to tunnel and Zener diodes but with lower operating voltages, used for rectification of small voltage signals.
- Avalanche Diode: Designed for the avalanche breakdown region, it’s similar to Zener diode but with a wider junction and higher breakdown voltage, used as a surge protector.
- Transient Voltage Suppression (TVS) Diode: Protects circuits from high voltage surges. It operates like an avalanche diode but can handle higher voltages.
- Gold Doped Diode: Uses gold or platinum as dopant for fast switching, but has a higher forward voltage drop and reverse leakage current.
- Constant Current Diode: Also known as current-limiting diode, it regulates the flow of current through it to a fixed level.
- Step Recovery Diode: Switches off current flow instantaneously when its direction is reversed, used in high-frequency applications.
- Peltier or Thermal Diode: Used for heat monitoring in microprocessors and cooling in refrigerators, due to its directional thermal resistance.
- Vacuum Diode: The simplest form of a diode, made from a vacuum tube, and used for rectification and signal detection.
- Varactor Diode: Acts as a voltage-controlled capacitor, used in phase-lock loops, RF tuning filters, and frequency multipliers.
- Gunn Diode: Used in oscillators for generating high-frequency microwaves, operates on the principle of negative resistance.
- PIN Diode: Used in high-voltage rectification and RF applications, acts as a linear resistor at high frequencies and as a rectifier at low frequencies.
- Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR): A four-layer P-N-P-N semiconductor device used for controlling high-power circuits and rectification.
- Shockley Diode: A four-layer PNPN diode, similar to SCR but without a control or gate input, used in switching applications.
- Point Contact Diode: Used for low voltage signal detection and in microwave mixers and detectors
Authorized Components Suppliers

Infineon Technologies
Founded in 1999, this German company specializes in manufacturing SMD diodes, with expertise in semiconductors and automotive systems. Infineon has branches in the USA, Japan, and Singapore, and manufactures various electronic components
Maxim Integrated
Established in 1983, Maxim Integrated is based in San Jose, California, and manufactures high-performance digital and analog electronic products, including mixed-signal products that enhance the design of smaller and more efficient systems

STMicroelectronics

Omron International
Founded as Tateisi Electric Manufacturing Company in 1993, Omron is a global leader in automation and a major manufacturer of SMD diodes and rectifiers. Headquartered in Kyoto, Japan, Omron operates in over 120 countries
NXP Semiconductors

Renesas Electronics
Highleap Electronic’s Advantages

Short procurement lead time
We can offer a quotation for you within 24 hours if you have prepared a comprehensive BOM list and correct PCB files. We have inventory support from our stable suppliers so that we can arrange the components within 3-5 days if they are in stock.
Cost-effective
We have years’ experience in PCB assembly and build a stable cooperative relationship with reliable component suppliers so that we can get the components at low costs. Price advantage can help you to lower the production cost.

supply chain management
We operate strict quality control standards and full supply chain management to make sure all the components are with the best quality and optimal price. We promise that all the components are subject to thorough incoming inspection and continuous testing during the entire production, and the procurement process is fully traceable.
Take a Quick Quote
Explore Highleap Electronic components sourcing Services.
