Resistors Sourcing
What are Resistors
Resistors are fundamental components in electronics, widely used to control or limit the flow of electric current in an electrical circuit. The resistance of a resistor determines how much it impedes the flow of electric current, A higher resistance means less current can flow for a given voltage, according to Ohm’s Law(V=IR), where V is voltage, I is current, and R is resistance.
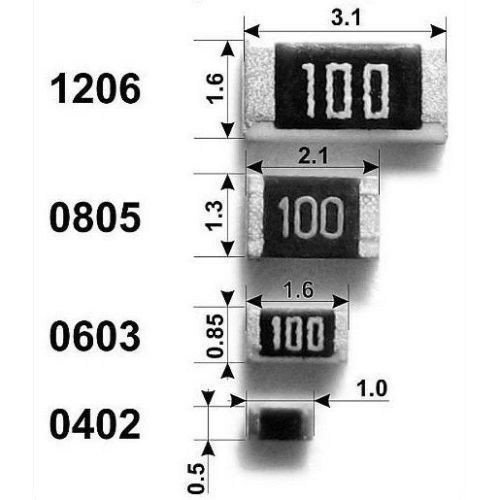
Kinds of Resistors
Resistors can be classified into different groups from different aspects:
Fixed Resistors
- Wire wound:
Made by winding a metal wire around a ceramic, plastic, or fiberglass core, known for high power ratings and precision but not suitable for high-frequency applications due to inductance.
- Carbon Composition:
Made of a mixture of carbon powder and a binding material, offering high pulse tolerance but with significant noise and variation with temperature and age.
- Carbon Film:
A thin carbon layer on a ceramic substrate, more stable than carbon composition resistors.
- Metal Film:
A thin metal layer on a non-conductive substrate, known for good temperature stability and lower noise.
- Metal Oxide Film:
Similar to metal film resistors but with better high-temperature performance.
- Thick and Thin Film:
Common in surface-mount technology; these resistors are made by depositing a conductive material on an insulating substrate.
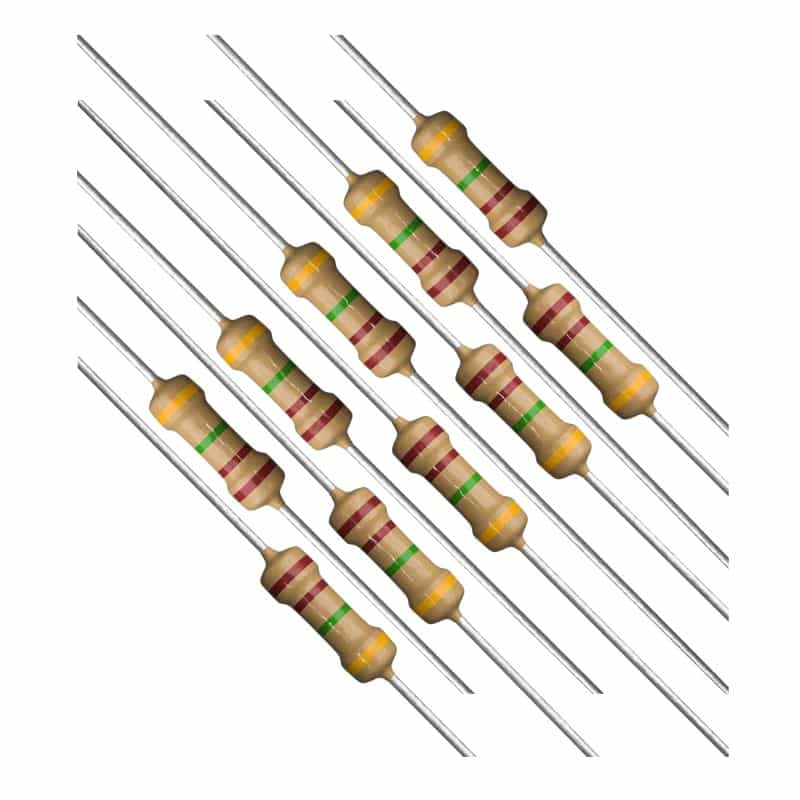
Variable Resistors
- Thermistors
Resistors whose resistance varies significantly with temperature. Used for temperature sensing and protection.
- Varistors / VDR (Voltage Dependent Resistors)
Resistors that change resistance with applied voltage, used for protecting circuits against voltage spikes.
- Photoresistors or LDRs (Light Dependent Resistors)
Change resistance with light intensity. Used in light sensing applications.
- Fusible Resistors
Designed to act as a fuse under overload conditions, providing both a resistor function and overcurrent protection.
Tips in Resistors Selection
Selecting the right resistor for a specific application is crucial for the proper functioning and reliability of an electronic circuit.
Resistance Value
Use Ohm’s Law (V=IR) and other circuit design principles to calculate the required resistance value.
Power Rating
Ensure the resistor can handle the power it will dissipate. Power rating is often given in watts (W), and a good rule of thumb is to choose a resistor with a power rating at least twice the expected power dissipation.
Tolerance
Tolerance indicates how much the actual resistance can vary from the stated value. Tighter tolerance is important for precision circuits, but it often comes with a higher cost.
Temperature Coefficient
This is crucial in applications where the resistor will experience temperature variations. A lower temperature coefficient means the resistance value changes less with temperature.
Size and Form Factor
In designs where space is limited, like in portable devices, the physical size of the resistor becomes an important consideration. Surface mount resistors are typically used in such applications.
Frequency Response
For high-frequency applications, avoid wirewound resistors, which can act inductively. Instead, opt for carbon, metal film, or other types with low inductance.
Noise Considerations
In sensitive audio or signal processing circuits, choose resistors with low noise specifications, like metal film resistors.
Special Requirements
If the circuit has special requirements like high surge currents (e.g., in power supplies) or needs a non-magnetic resistor (e.g., in medical imaging equipment), make sure to select a resistor type that meets these needs.
- Variable Resistors:
For applications requiring tunable resistance, consider the type of variable resistor (potentiometer, trimmer, or rheostat) based on the adjustment range, precision, and physical size. - Safety Margins:
Always design with safety margins in mind, considering potential over-voltages or over-currents that could exceed the normal operating conditions.
Authorized Components Suppliers

Vishay
A major global manufacturer known for a wide range of electronic components including resistors.

Yageo
Yageo is a leading global supplier of passive components, including a comprehensive range of resistors.

TE Connectivity
Formerly Tyco Electronics, they offer high-quality electronic components, including resistors suited for demanding applications.

Murata
A major manufacturer of electronic components, including high-quality resistors, particularly known for their surface-mount devices.

Ohmite
With a history dating back to the 1920s, Ohmite manufactures resistors for high-power applications, among other electronic components.

KOA Speer
Specializing in passive components, KOA Speer offers a variety of resistors, known for their reliability and precision.
Highleap Electronic’s Advantages

Short procurement lead time
We can offer a quotation for you within 24 hours if you have prepared a comprehensive BOM list and correct PCB files. We have inventory support from our stable suppliers so that we can arrange the components within 3-5 days if they are in stock.
Cost-effective
We have years’ experience in PCB assembly and build a stable cooperative relationship with reliable component suppliers so that we can get the components at low costs. Price advantage can help you to lower the production cost.

supply chain management
We operate strict quality control standards and full supply chain management to make sure all the components are with the best quality and optimal price. We promise that all the components are subject to thorough incoming inspection and continuous testing during the entire production, and the procurement process is fully traceable.
Take a Quick Quote
Explore Highleap Electronic components sourcing Services.
