Inductors
What are Inductors
Inductors, often symbolized with a coiled wire in circuit diagrams, works on the principle of electromagnetism. Inductors resist changes in current flow, which is described as inductive reactance. This reactance increases with frequency, making inductors behave as short circuits in DC conditions and as open circuits at high frequencies. Inductors mainly play the functions of filtering, oscillation, delay and notch in the circuit, as well as filtering signals, filtering noise, stabilizing current and suppressing electromagnetic wave interference.
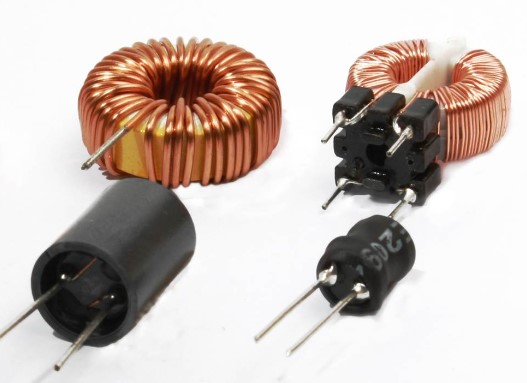
Kinds of inductors
Inductors can be classified into different groups from different aspects:
Air Core Inductors:
These inductors do not have a core; the coil is wound in the air. They have low inductance values but are free from core losses and saturation.
Ferrite Core Inductors:
Made with a core of ferrite material, which increases the inductance. They are commonly used in high-frequency applications like RF (Radio Frequency) circuits.
Iron Core Inductors:
These have an iron core and provide higher inductance values than air core inductors. They are often used in low-frequency applications, like power supplies.
Toroidal Inductors:
Wound on a doughnut-shaped core, toroidal inductors are efficient with minimal electromagnetic interference. They are preferred in sensitive circuits.
Variable Inductors:
Designed to allow adjustment of the inductance value, often by moving a ferrite core in or out of the coil.
RF Inductors:
Specifically designed for radio frequency applications, these inductors have low resistance to maintain high Q factor (quality factor) at high frequencies.
Choke Coils:
A type of inductor used to block high-frequency AC signals while allowing DC to pass through. They are often used in power supply filtering.
Laminated Core Inductors:
Constructed with laminated iron cores to reduce eddy current losses, making them suitable for low-frequency applications like audio circuits.
Molded Inductors:
Encased in a molded plastic shell, these inductors offer protection and durability, often used in automotive and industrial electronics.
SMD (Surface Mount Device) Inductors:
Designed for surface mounting on PCBs, these inductors are used in compact electronic devices.
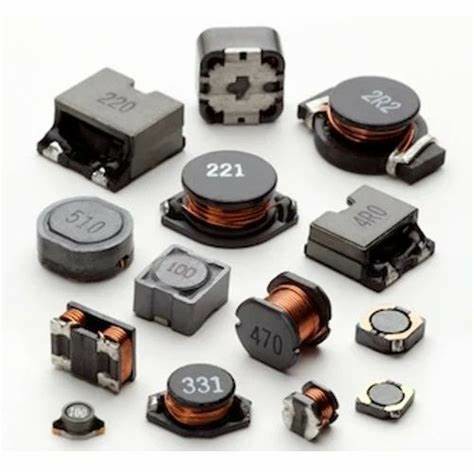

Tips in Inductors Selection
Selecting the right Inductors for a specific application is crucial for the proper functioning and reliability of an electronic circuit.
Required Inductance
Based on the circuit’s requirements, calculate the necessary inductance, typically measured in henries (H), but more often in millihenries (mH) or microhenries (µH) in practical circuits.
Current Rating
The inductor must be able to handle the maximum current that will flow through it without saturating. Ensure the inductor’s current rating is higher than the peak current in your circuit.
DC Resistance
The DC resistance of the inductor affects the efficiency of the circuit. Lower DCR is generally better, especially in power applications, as it reduces power losses.
Frequency Response
Consider the operating frequency of your circuit. Different inductors perform differently at various frequencies, especially regarding their inductive reactance and Q factor (quality factor).
Authorized Components Suppliers

Murata
A major manufacturer of electronic components, including high-quality resistors, particularly known for their surface-mount devices.

TDK Corporation
Offers a wide range of inductors, including power inductors, RF inductors, and chip inductors, known for their reliability and performance.

Vishay
A major global manufacturer known for a wide range of electronic components including resistors.

KEMET Corporation
Offers a broad portfolio of inductors, including ferrite and film inductors, suitable for a range of applications.

Bourns
Maxim Integrated
Highleap Electronic’s Advantages

Short procurement lead time
We can offer a quotation for you within 24 hours if you have prepared a comprehensive BOM list and correct PCB files. We have inventory support from our stable suppliers so that we can arrange the components within 3-5 days if they are in stock.
Cost-effective
We have years’ experience in PCB assembly and build a stable cooperative relationship with reliable component suppliers so that we can get the components at low costs. Price advantage can help you to lower the production cost.

supply chain management
We operate strict quality control standards and full supply chain management to make sure all the components are with the best quality and optimal price. We promise that all the components are subject to thorough incoming inspection and continuous testing during the entire production, and the procurement process is fully traceable.
Take a Quick Quote
Explore Highleap Electronic components sourcing Services.
