METAL CORE PCB
Robust and Durable, Highleap’s metal core PCBs help you achieve exceptional product performance!
What is a Metal Core PCB
Metal Core Printed Circuit Board (MCPCB), also known as insulated metal substrate (IMS) PCB and thermal PCB.Metal Core Printed Circuit Boards (MCPCBs) are a specialized type of printed circuit board designed for enhanced thermal management and heat dissipation performance.
Unlike standard FR4 PCBs, MCPCBs utilize a metal base layer as the core substrate instead of fiberglass composites. Common metal core materials include aluminum, copper, and alloy steels. The high thermal conductivity of the metal core enables efficient spreading and sinking of heat away from critical components mounted on the board. This allows MCPCBs to handle higher power densities compared to traditional FR4.
The metal core is insulated from the outer circuit layers by direct bonded ceramic dielectric layers. These dielectric coatings are typically made of materials like aluminum oxide, aluminum nitride, or beryllium oxide chosen for their electrical insulating properties and high thermal conductivity. This prevents electrical shorts between the core and circuits while facilitating heat transfer through the base.
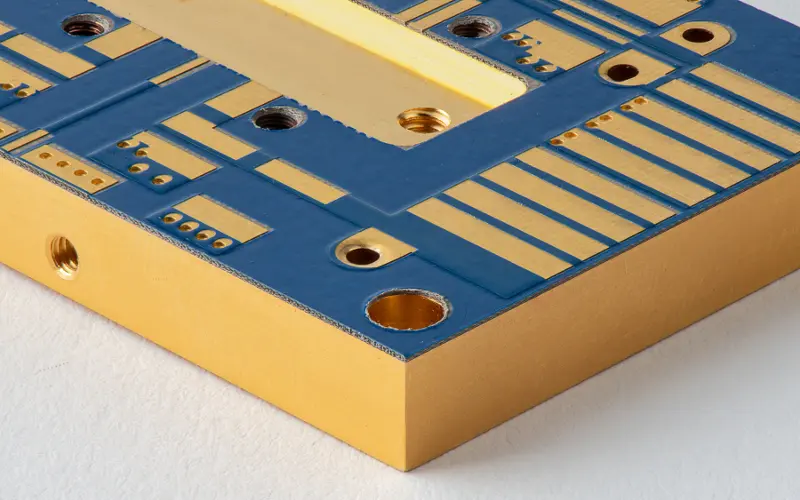
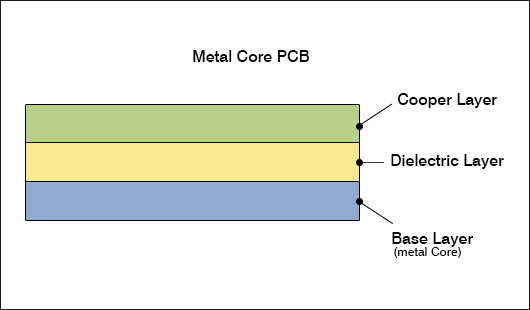
The structure of MCPCB
Metal Core PCBs comprise three crucial layers: a metal core, dielectric layer, and copper layer. This unique structure optimizes heat dissipation, enhancing overall performance and reliability of electronic systems.
The metal core, typically aluminum or copper, boasts high thermal conductivity and mechanical strength. Acting as a heat sink, it efficiently conducts and spreads heat away from components, maintaining optimal operating temperatures and preventing thermal damage.
The dielectric layer, bonded to the metal core, provides electrical insulation and thermal management properties. Crafted from materials with enhanced thermal conductivity, it facilitates efficient heat transfer from components to the metal core. The dielectric layer ensures even heat distribution, minimizing hotspots and thermal stress.
Advantages of MCPCB
Metal Core PCBs (MCPCB) features that make them ideal for high power and high temperature electronics applications:
Metal Core PCBs offer superior cooling, improved reliability and simplified thermal design – making them the ideal choice for high power LED lighting, automotive electronics, power conversion modules, etc.
A New Era in Heat Dissipation, Highleap Has You Covered! Our metal core PCBs, opening a new chapter in thermal management.
Superior Thermal Performance
- The thick metal core provides an excellent heat spreading platform to quickly conduct heat away from components. This allows effective cooling of LEDs, power devices, etc.
- The dielectric layer ensures efficient heat transfer from the component pads/traces to the metal core while electrically isolating the circuits.
- Thermal vias help transfer heat from the circuits to the metal baseplate.
- Overall highly effective thermal management by reducing thermal resistance.
Enhanced Reliability
- Consistent operating temperature prevents thermo-mechanical stress on components.
- Less prone to delamination, micro-cracks and failures caused by overheating.
- Withstands higher operating temperatures and temperature cycling.
- Longer product lifetimes and reduced failures.
Simplified PCB Design
- Allows incorporation of both circuitry and heatsinking in one board.
- Eliminates the need for additional heat sinks and thermal interface materials.
- Components can be directly soldered onto the board without insulation pads.
- Dense component layouts possible owing to efficient cooling.
- Thicker boards provide enhanced structural rigidity.
Main Types of Metal Core PCBs
There are three main types of Metal Core PCBs (MCPCBs) based on the choice of metal core material:
Aluminum Core PCBs
These MCPCBs have an aluminum core, which is lightweight, cost-effective, and offers good thermal conductivity. Aluminum core PCBs are widely used in various applications, including LED lighting, automotive electronics, and power electronics.
Copper Core PCBs
MCPCBs with a copper core provide excellent thermal conductivity, making them suitable for high-power applications that require efficient heat dissipation. Copper core PCBs are commonly used in high-performance computing, telecommunications, and industrial equipment.
Mixed Metal Core PCBs
Some MCPCBs feature a mixed metal core, combining the advantages of different metals. For example, a mixed metal core may include a copper layer for enhanced heat dissipation and an aluminum layer for cost-effectiveness. These mixed metal core PCBs offer a balance between performance and cost, catering to specific application requirements.
Aluminum PCB VS Copper base PCB
Aluminum base PCBs
- With good thermal conductivity of 237W/mK, aluminum meets most heat dissipation requirements.
- Aluminum is relatively inexpensive, reducing overall material costs.
- Aluminum is easier to fabricate, allowing mechanical drilling and processing.
- Lightweight aluminum enables lightweight electronic designs with density below 3g/cm3.
- Mature aluminum surface treatments like anodizing and coating are available.
- Aluminum has poor corrosion resistance requiring extra protection. It is suitable for regular commercial environments

Copper base PCBs
- Excellent 393W/mK thermal conductivity makes copper ideal for high power devices.
- Copper is difficult to fabricate, not machinable, needs precision process control.
- Though pricier than aluminum, copper is cost-effective for extreme heat dissipation.
- High 8.8g/cm3 density makes copper heavy requiring structural support.
- Excellent corrosion resistance allows copper PCBs to be used in harsh environments.
- Gold, silver plating improves soldering and assembly for copper PCBs.
Applications of Metal Core PCBs
Metal core PCBs have various applications, mainly in areas that require:
High power
They can dissipate more power due to the metal core, so they are used in high power applications like switching power supplies, motor controls, etc.
High heat flux
The thermal conductivity of the metal core helps quickly dissipate large amounts of heat generated in areas like CPU boards, power amplifier circuit boards, etc.
High reliability
The even temperature distribution and reduced thermal stresses improve the reliability of electronics, so used in industrial/military applications.
Miniaturization
The smaller trace widths allow higher density packing of components, useful in applications like embedded systems.
High electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding
The metal core acts as a Faraday cage, shielding the internal electronics from EMI. Used in applications like RF circuits.
High data transmission rates
The shorter, fatter traces have lower impedance and losses at high frequencies, suitable for high speed data transmission circuits.
Some specific examples of metal core PCB applications:
- Power supplies
- Motor controls
- RF circuits
- CPU boards
- Power amplifiers
- Embedded systems
- Avionics and spacecraft circuit boards
- Military and industrial electronic systems
The difference between metal core PCB and FR4 PCB
Thermal conductivity: MCPCB has a metal core, with much better heat dissipation performance than FR4 PCB.
Service life: Due to better heat dissipation, the service life of MCPCB is generally longer than FR4 PCB.
EMI shielding: The metal core of MCPCB can shield electromagnetic interference, with stronger anti-interference capability.
Conductivity: The metal core (usually copper or aluminum) of MCPCB has higher conductivity.
Density: MCPCB can achieve a more compact circuit layout and smaller transmission line gaps, so the density is higher.
Mechanical strength: The metal core board of MCPCB is usually harder and stronger than FR4 substrate.
Cost: The cost of MCPCB is generally higher than common FR4 PCB.
Application scope: MCPCB is suitable for applications requiring high power, high density, high speed and high reliability, such as high-end servers and professional test equipment. FR4 PCB is widely used in various general electronic devices.
In summary, MCPCBs offer several advantages over FR4 PCBs, including superior heat dissipation, higher thermal conductivity, and stronger EMI shielding. However, it’s important to note that MCPCBs generally come at a higher cost. The selection between the two depends on the specific technical requirements of the application.
Worry-free Heat Dissipation, Highleap Has You Covered! Our metal core PCBs, the perfect choice for thermal management.
Metal Core PCB Design Guidelines
Thermal Management
The metal core in MCPCBs provides a highly conductive path for heat dissipation. To ensure efficient heat transfer, it is essential to design the board with proper thermal vias, thermal pads, and heatsinks. The thermal vias should be located in close proximity to the heat-generating components and should be of sufficient size to provide low thermal resistance.
Material Selection
Carefully select the metal core material to optimize MCPCB performance. Aluminum is commonly used for its high thermal conductivity, cost-effectiveness, and lightweight properties. However, copper, brass, or stainless steel can be considered based on specific application requirements. Additionally, the dielectric material and copper thickness impact overall board performance.
Trace Width and Spacing
Design appropriate trace width and spacing to handle current carrying capacity and maintain signal integrity. Ensure the trace width is sufficient to carry the required current without generating excessive heat. Adequate spacing between traces minimizes signal interference and crosstalk. Set minimum trace width and spacing based on manufacturing processes and application needs.
Component Placement
The placement of components on MCPCBs is critical for both thermal management and signal integrity. High-power components should be placed close to the metal core to maximize heat dissipation, while sensitive components such as RF circuits should be placed away from the heat source. The component density should be optimized to ensure efficient use of board space and to avoid signal interference.
Solder Mask
The solder mask on MCPCBs should be designed to facilitate thermal transfer while providing insulation between traces. Choose a solder mask with a matte finish, as it offers improved thermal conductivity. Ensure proper clearance and coverage to prevent solder bridging and short circuits. A well-designed solder mask enhances performance and reliability.
Final Considerations
In addition to the above guidelines, pay attention to factors such as EMC considerations, environmental requirements, and manufacturing capabilities. Ensure compliance with relevant industry standards. Collaborate closely with your PCB manufacturer to optimize design and manufacturing processes for MCPCBs, ensuring superior performance, reliability, and customer satisfaction.
Looking for a Metal Core PCB Quote?
With extensive experience in the PCB manufacturing industry, Highleap possesses abundant knowledge. We are highly proficient in the design and production of Metal Core PCBs, ensuring high-quality outcomes.

Highleap excels in Metal Core PCB manufacturing with cutting-edge technology, ensuring precision for high-power electronic devices’ exceptional thermal performance.

Choose Highleap for top-notch customer service. Prompt technical support ensures swift issue resolution. Collaborate closely with us to meet your personalized requirements and exceed expectations!
Take a Quick Quote
Discover how our expertise can help with your next PCB project.
