Back to blog
Complete PCB SMT Assembly Process Flow
Print Solder Paste
The first step in the PCB SMT assembly process is applying solder paste to the PCB. A stencil is used to precisely deposit the paste only on the pads where components will be placed. This paste acts as an adhesive and solder source for attaching components.
PCB & PCBA quick quote
Related Articles
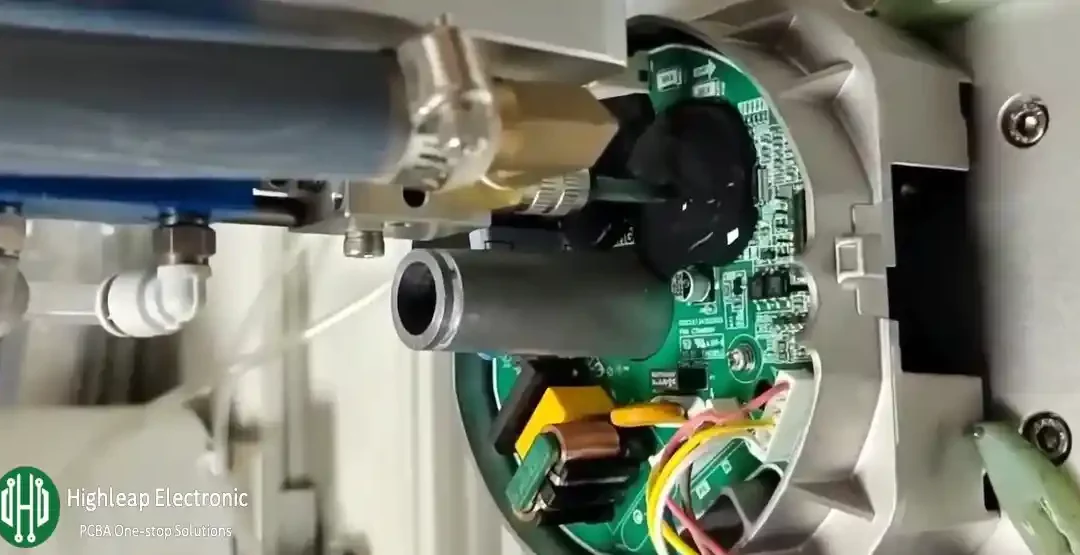

How to Select the Best PCB Encapsulation Material for Your Project
PCB Encapsulation-PCB PottingIntroduction to Potting and Encapsulation Potting or encapsulation is a widely used method to protect circuit boards from damage, and it has proven to be effective. Different potting compounds are used in various circuit environments,...
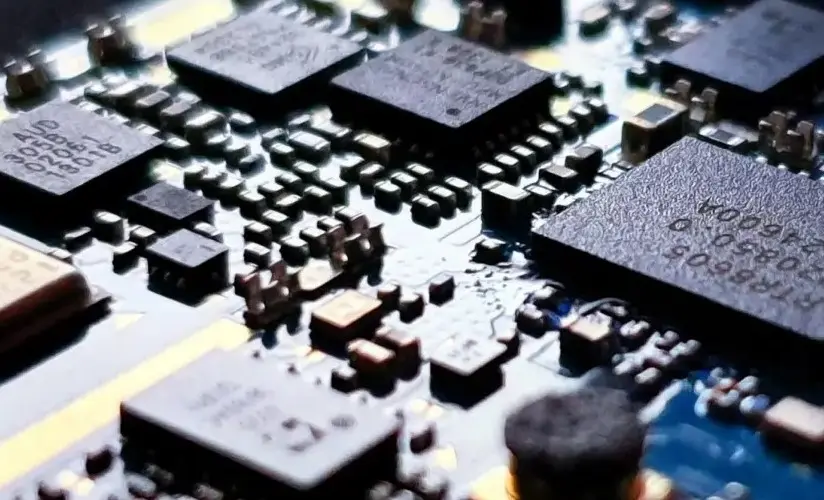

What is the difference between SMD and SMT?
PCB SMTIntroduction to SMT and SMD Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Surface Mount Devices (SMD) are crucial concepts in the field of electronics manufacturing, specifically in the assembly of printed circuit boards (PCBs). Both terms are integral to the modern...


Flexible PCB Cost Optimization Strategy
flexible PCBIn the realm of contemporary electronics, the proliferation of flexible PCBs stands as a testament to the industry's evolution toward miniaturization and functionality. Unlike the more traditional rigid PCBs, which benefit from simpler production...
Take a Quick Quote

