Back to blog
A Comprehensive Guide to Electronic Manufacturing Services
Electronic manufacturing services (EMS) refer to companies that provide end-to-end services for the design, development, testing, manufacturing, and support of electronic components, printed circuit boards (PCBs), and complete electronic devices. EMS providers are essentially contract manufacturers that work with original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and other companies that do not have internal manufacturing capabilities.
The global EMS market was valued at $455 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $775 billion by 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 6.2% from 2023 to 2030 according to Emergen Research. This growth can be attributed to several key factors:
- Increasing demand for consumer electronics and wearables: Smartphones, tablets, smart wearables, home appliances, and other electronics are driving much of the growth. For example, smartphone shipments reached 1.35 billion units in 2022.
- Vehicle electrification: The electric vehicle market is expanding rapidly, reaching over 10 million EVs on the road globally in 2022. These require considerable electronics manufacturing capabilities.
- Advances in technology: 5G networks, AI, IoT, VR/AR, and other emerging technologies require sophisticated electronics and trusted manufacturing partners.
- Focus on core competencies: OEMs are increasingly outsourcing manufacturing to focus internal resources on design, branding, and intellectual property.
- Supply chain efficiencies: EMS provides economies of scale in procurement, manufacturing, and logistics.
This guide provides an in-depth look at electronic manufacturing services, including the range of services offered, the benefits of partnering with EMS providers, how to select the right partner, key technologies and processes, market trends, and more.
What Services Do Electronic Manufacturing Service Providers Offer?
EMS companies provide a very broad range of services related to taking an electronic product from concept to production. Here are some of the most common:
Design Services
- Product concept consultation
- Industrial design
- Mechanical engineering design
- PCB layout and design
- Firmware and embedded software development
Prototype Services
- PCB prototyping
- 3D printing of enclosures
- Limited test runs
Testing Services
- Design verification testing
- In-circuit testing
- Functional testing
- Environmental testing (temperature, humidity, vibration, etc.)
- Compliance testing
- Reliability testing
Manufacturing Services
- PCB fabrication and population
- Plastic injection molding
- Metal fabrication and finishing
- Final assembly and integration
- SMT assembly
- Supply chain management
- Inventory management
Post-Manufacturing Services
- Order fulfillment and logistics
- Repair and replacement
- Warranty and maintenance
- End-of-life support
Leading EMS companies have expertise across this entire spectrum of services required to take a product from idea to high-volume production. They provide a “one-stop shop” for electronics makers who do not have in-house manufacturing capabilities.
Key Benefits of Using EMS Providers
There are several compelling reasons for OEMs and electronics companies to partner with EMS providers rather than manufacture products completely in-house:
Cost Savings
EMS providers achieve significant economies of scale in procurement, manufacturing, and logistics that can result in dramatically lower per unit costs compared to in-house manufacturing. Their expertise also results in higher yields and lower scrap.
Focus on Core Competencies
Rather than investing in manufacturing infrastructure and expertise, OEMs can focus internal resources on product design, software, branding, and intellectual property – their true core competencies.
Speed and Agility
By leveraging the expertise, capacity, and supply chain networks of EMS partners, products can get to market significantly faster. EMS providers can also scale production up or down more quickly.
Access to Advanced Technology
Top EMS companies invest heavily in staying at the leading edge of manufacturing technologies such as automation, AI/ML, simulation, and advanced quality control systems. Their customers benefit from access to advanced capabilities.
Supply Chain Efficiencies
EMS providers have established global supply chains and centralized procurement capabilities that are extremely efficient compared to managing this in-house. They have preferred supplier relationships, purchasing power, and logistics expertise.
Flexibility and Scalability
EMS provides the flexibility to quickly ramp production up or down based on changing demand. Companies can scale without having to invest in their own capital equipment and facilities.
By leveraging EMS, OEMs can minimize risk, get products to market faster, scale efficiently, and focus resources in the areas where they can provide the most value. The EMS industry has expanded rapidly based on these benefits.
Best Practices for Selecting an EMS Partner
Since EMS providers essentially become an extension of your team, it is important to select the right partner. Here are some best practices:
Understand Your Requirements
First, detail your specific needs in areas like design collaboration, prototyping services, volume requirements, quality expectations, compliance standards, post-manufacturing support needs, and total cost targets. Share these with prospective EMS partners.
Target EMS Expertise
Find EMS companies with specific expertise in your industry and technology area. For example, some specialize in medical devices, high-reliability electronics, automotive, etc.
Request References
Ask for references from current customers with projects similar to yours and contact them to understand their experience.
Tour Facilities
Visit candidate facilities to view capabilities and processes first-hand and meet engineering teams.
Compare Quality Processes
Review the testing, quality control, and reliability procedures implemented by each provider. Certifications like ISO, industry-specific standards, and others can serve as useful benchmarks.
Evaluate Services
Consider the full range of services offered to determine if the provider can meet all your needs from early prototyping through post-manufacturing support.
Consider Location
Factor geography into the decision based on logistics needs, ability to visit facilities, travel time for engineering collaboration, and other requirements.
Assess Cultural Fit
Since you will work closely together, make sure your teams and processes align well for smooth collaboration. Compare approaches to project management, communication styles, and problem resolution.
By carefully vetting EMS partners, OEMs can find the right fit for their specific manufacturing needs and set the stage for a successful long-term partnership.
An Overview of Key Manufacturing Technologies and Processes
EMS companies utilize a variety of sophisticated design, testing, manufacturing, and quality control technologies and processes. Here is an introduction to some of the most essential ones.
Printed Circuit Board Assembly
PCB assembly, also called PCBA, is the process of soldering electronic components onto a PCB. This includes surface mount components (SMT) as well as through-hole components. Automated SMT assembly lines efficiently place tiny surface mount parts with extreme precision using solder paste and reflow soldering. For through-hole parts, wave soldering makes connections. Complex PCBs require extensive testing.
In-Circuit Test (ICT)
ICT tools use “bed-of-nails” test fixtures to electrically probe a loaded PCB and validate the integrity of circuits, components, and solder joints. Any defects or wrong parts can be identified. Flying probe testers provide non-contact testing.
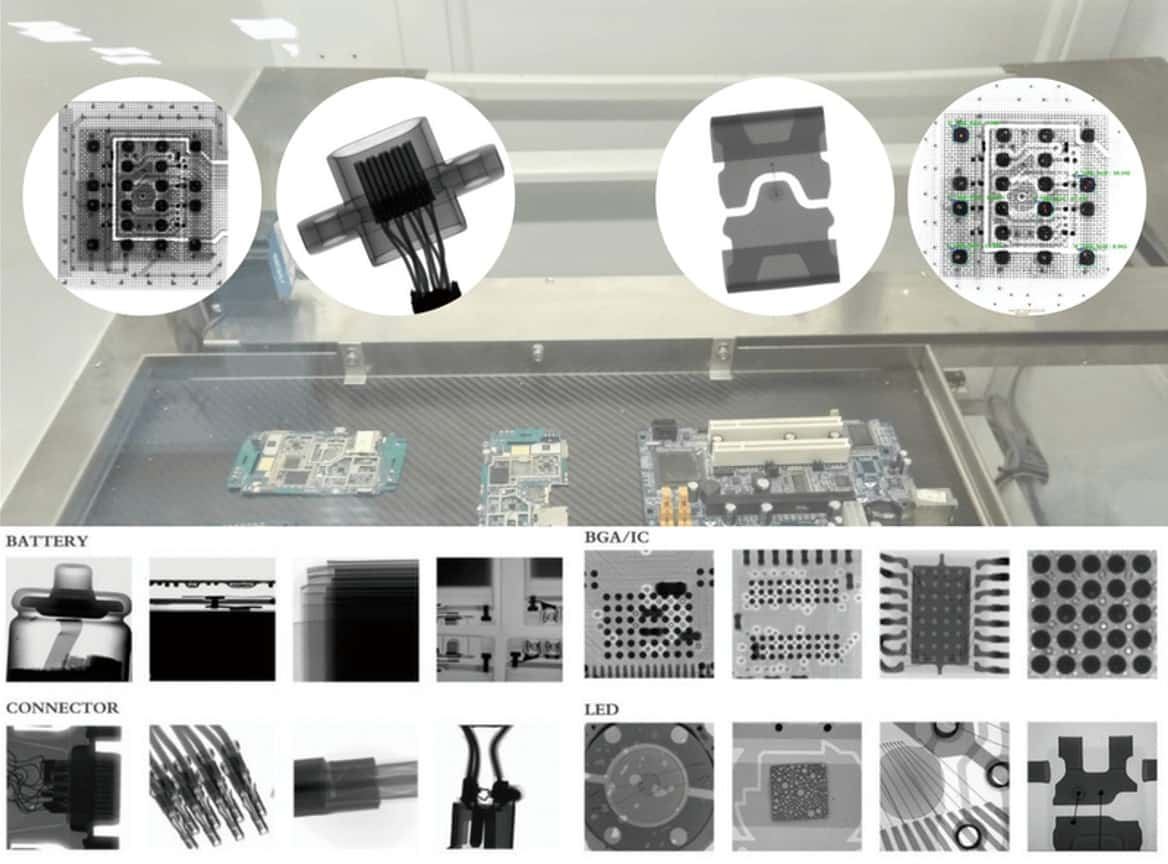
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
AOI systems use high-resolution cameras to visually inspect PCB assemblies and identify defects such as missing or misaligned components, poor solder joints, and board damage. Some systems also use X-ray imaging. AOI acts as a key quality control step.
Functional Test (FT)
Functional testing validates the finished board or system by stimulating inputs and monitoring outputs. This confirms proper integrated circuit operation and successful PCB assembly prior to final assembly. FT can be manual or automated.
Environmental Stress Screening (ESS)
ESS exposes systems to extreme conditions such as temperature, vibration, and humidity to force latent defects to manifest themselves. This “burn-in” testing improves reliability andcatchies issues before products ship.
Failure Analysis
When defects occur, failure analysis lab techniques like scanning acoustic microscopy, electron microscopy, and fourier transform infrared spectroscopy help determine root causes so corrective actions can be implemented.
Statistical Process Control (SPC)
SPC monitors processes using statistical methods to detect significant variances from targets. Control charts track critical parameters, identifying stability issues. This allows preventive action to avoid potential defects.
These and other sophisticated technologies and processes enable EMS providers to meet the quality, reliability, and efficiency demands of electronics manufacturing. Continuous improvement is also critical.
Key Industry Trends Shaping Electronics Manufacturing
EMS companies must stay on the leading edge of technologies and strategies to meet the evolving needs of OEMs. Here are some impactful industry trends:
Internet of Things
By 2030 there could be over 30 billion connected IoT devices worldwide. Supporting the boom in smart, connected products is driving major shifts in EMS.
Industry 4.0
The rise of smart factories and supply chains leveraging automation, AI, industrial IoT, and big data analytics is transforming electronics manufacturing.
Advanced Packaging
Innovations in semiconductor packaging, such as 2.5D/3D stacking using through-silicon vias, allow greater functionality in smaller form factors.
Sustainability
E-waste is a growing concern. EMS providers are helping meet robust sustainability goals through near-zero waste manufacturing, renewable energy, and material innovations.
Supply Chain Resilience
Recent disruptions have underscored the importance of supply chain visibility, flexibility, and redundancy. EMS providers play a key role in mitigation strategies.
Lifecycle Management
With rapid product cycles, EMS supports OEMs with end-of-life planning including last-time buys of obsolete parts and redesign expertise.
Smart Factories
AI, advanced automation, augmented reality, big data, and more enable “lights out” smart factories with minimal human intervention, driving major quality and efficiency gains.
With deep expertise in manufacturing technology, EMS companies play a vital role in turning these trends into competitive advantages for their customers through collaboration, constant innovation, and disciplined execution.
The Importance of Prototyping Services
A key capability offered by most EMS providers is low-volume PCB assembly for prototype boards, pilot builds, and pre-production verification. Prototyping provides enormous benefits:
- Validation of design – Building working prototypes allows real-world testing to identify issues early before design finalization. Items like manufacturability, usability, and reliability can be evaluated.
- Proof of concept – Demonstrate the basic functionality and technology viability of a new product idea with working prototypes.
- Iterative refinement – Test, identify issues, refine, and re-prototype rapidly to converge on an optimized design.
- Evaluation of alternatives – Experiment with different design approaches, component selection etc. and realize what works best.
- Cost reduction – Optimization during iterative prototyping typically yields significant cost savings for final production.
- Risk reduction – Finding and fixing problems early avoids costly delays and defects during high-volume manufacturing.
- Time-to-market acceleration – Getting working prototypes early speeds up development, testing, certification, and launch.
EMS prototyping combined with OEM engineering expertise helps maximize first-time production success. This capability will continue growing in importance with pressures for faster development cycles.
The Critical Role of Quality Control
Given the mission-critical nature of many electronic systems, quality is paramount in EMS. Superior quality yields lower total cost through increased production yield, improved reliability, reduced rework, and avoidance of reputational damage. Here are some of the ways top-tier EMS companies achieve excellence in quality:
Advanced Inspection Technologies
As covered earlier, automated optical, X-ray, and electrical inspections quickly identify assembly issues or component defects. Machine vision and AI enable unprecedented quality vigilance.
Comprehensive Testing
Rigorous testing methodologies validate functionality, performance, reliability, environmental resilience, standards compliance, and more while guarding against corner-cutting.
Process Controls
Statistical process control, production monitoring, corrective actions, control plans, traceability systems, change management, and training are ingrained. Zero-defect mentalities prevail.
Certifications
Compliance with stringent industry and regulatory quality standards like ISO, IATF 16949, AS9100, and FDA regulations validate capabilities.
Expert Engineers
Skilled engineers specialized in disciplines like design for manufacturing, reliability, test, and quality engineering provide oversight and optimization.
Customer Collaboration
Close customer collaboration during design, prototyping, pilot builds, testing, and process validation ensures requirements are met and prevented defects.
Continuous Improvement
Relentless efforts to refine processes, upgrade technology, enhance training, implement best practices, and adopt automation enable steady quality gains over time.
EMS providers invest heavily in these critical capabilities to meet the exacting demands of the electronics industry while minimizing risks and costs for their OEM customers.
Navigating Industry Challenges
While the EMS industry continues to expand globally based on its many benefits, EMS companies and their customers also face an array of challenges that must be managed:
Component Shortages
Recent shortages of key ICs, passive components, substrates, etc. have made procurement difficult. EMS providers play a key role through demand planning, buffers, substitution flexibility, and supply chain resilience.
Geopolitical Factors
Trade disputes, export controls, sanctions, and other geopolitical issues can constrain access to certain markets and technologies. Agile EMS partners help OEMs adapt.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Natural disasters, logistics bottlenecks, plant closures, and other disruptions require supply chain agility and redundancy. Multi-site EMS can mitigate localized impacts.
Compliance Complexity
Meeting standards, regulations, and legal requirements across different regions and markets demands diligent processes and expertise. EMS providers offer valuable compliance support.
Quality Excursions
Despite best efforts, some percentage of defects occur. Swift containment, root cause analysis, corrective actions, and customer partnership enable effective resolution.
Intellectual Property Protection
OEMs must safeguard proprietary technology and IP during EMS collaboration while allowing the access needed for efficient manufacturing and technical problem solving.
Margin Pressures
Although economies of scale are substantial, EMS margins remain tight. Innovation in automation, materials, testing, simulation, and data analysis drive further efficiency gains.
By proactively addressing these challenges in partnership with OEMs, EMS companies can strengthen resilience while improving performance, quality, and customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
The services offered by electronic manufacturing service providers encompass the entire journey of taking an electronic product from concept to high-volume production to end-of-life.
EMS offers OEMs and technology companies compelling advantages in cost, speed, quality, scalability, and added capabilities while allowing a focus on core competencies.
Careful selection of EMS partners along with close collaboration enables customers to leverage manufacturing excellence, deep expertise, and lessons learned from diverse industries. This accelerates innovation and time-to-market while reducing risks and costs.
Continued technology advances such as smart factories, supply chain digitization, autonomous optimization, and sustainable manufacturing will enable EMS providers to deliver still greater value as trusted partners serving the rapidly evolving electronics industry.
Related Articles

Smart Fingerprint Locks: Technology Demand Analysis
Fingerprint locksIn our digitally-driven era, the demand for secure yet convenient access control systems has propelled biometric security to the forefront. Among these, fingerprint locks have emerged as a preferred choice, offering a seamless blend of sophisticated...

Top 25 USA Electronics Manufacturing Companies in 2024
Highleap Electronics ManufacturingThe United States boasts a robust electronic manufacturing industry, with numerous companies dedicated to developing and producing various complex electronic systems, components, and devices. Its advanced manufacturing infrastructure,...
PCB Meaning: Definition, Functionality, and Applications
PCB design drawingIn the digital age, the functionality and efficiency of electronic devices hinge largely on the hidden yet crucial components they comprise. Among these, Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are foundational, underpinning the vast landscape of modern...
Take a Quick Quote