Back to blog
Reliable PCBs: The Role of Functional Circuit Testing
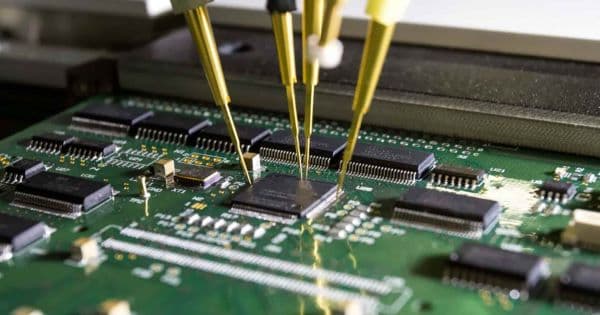
Functional Circuit Testing
In the realm of Printed Circuit Board (PCB) manufacturing, ensuring the functionality and reliability of the boards is paramount. Functional Circuit Test (FCT) is a crucial step in this process, serving as the final check before the boards are released into the market. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of FCT, its importance in PCB assembly, and how it contributes to the overall quality assurance of electronic products.
Understanding the Role of FCT in PCB Manufacturing
Functional Circuit Test (FCT) is a critical part of the PCB manufacturing process, serving as the final quality check before products are released to the market. FCT involves testing the functionality and integrity of a PCB by stimulating its input and output signals, such as voltage, current, and power, to assess the response of its components. This test ensures that all elements are working as intended, properly connected, and compliant with the required standards.
Importance of Functional Circuit Testing (FCT) in PCB Manufacturing
Functional Circuit Test (FCT) plays a crucial role in ensuring the quality and reliability of printed circuit boards (PCBs) before they are released into the market. As the final step in the PCB manufacturing process, FCT serves as a comprehensive quality check that verifies the functionality and integrity of the PCB.
During FCT, the PCB is subjected to a series of tests that stimulate its input and output signals, including voltage, current, and power. These tests are designed to assess the response of the PCB’s components and ensure that they are working as intended. By evaluating the PCB’s performance under simulated operating conditions, FCT helps to identify any potential issues or defects that could affect its functionality in real-world applications.
One of the key objectives of FCT is to ensure that all elements of the PCB are properly connected and compliant with the required standards. This includes verifying the correct placement and orientation of components, as well as checking for any soldering defects or electrical shorts. By performing these tests, manufacturers can identify and rectify any issues before the PCBs are released for mass production.
Overall, FCT plays a critical role in ensuring the quality and reliability of PCBs, helping to prevent costly recalls and ensuring that electronic products perform as expected in the field.
PCB functional testing video demonstrating our rigorous electrical testing process to ensure the quality and reliability of every PCB.
The Comprehensive Process of FCT in PCB Manufacturing
The FCT process begins with meticulous planning, where manufacturers determine which tests to run based on the PCB design and application requirements. This may include power-on tests, logic tests, and signal integrity tests. Once the testing plan is established, the actual FCT is conducted using specialized equipment such as an oscilloscope or logic analyzer to measure the PCB’s response to input signals.
During the test, operators visually inspect the board for any physical defects and use test fixtures to connect the board to the test equipment. The test software manages the test process and collects key information, ensuring that all elements are tested accurately and reliably. Any issues identified during the test are isolated and corrected before the board is released for further production operations.
Classification of PCB FCT Testing
FCT testing can be classified based on control mode and controller type, each offering distinct advantages and applications in the PCB manufacturing process.
Control Mode:
- Manual: Operators manually control the testing process, which can be time-consuming and labor-intensive but may be suitable for low-volume production or specialized testing requirements.
- Semi-automatic: A combination of manual and automated control, where some aspects of the testing process are automated, but operators still have some control over the testing process.
- Fully automated: The most efficient and commonly used mode, where the entire testing process is automated, leading to increased production efficiency and consistency.
Controller Type:
- MCU controller and Embedded CPU controller: These controllers offer quick and easy functional circuit testing for specialized circuits and programs, providing highly precise test solutions.
- PC Controller: The most commonly used controller type, leveraging the accessibility and affordability of PC technology. It allows for easy data output and file processing of test results on a workstation’s operating system, simplifying the overall testing process.
- PLC Controller: Primarily used in professional industrial control, PLC controllers focus on regulating the induction component in standard FCT testing, offering a robust and reliable solution for industrial applications.
Manufacturers must ensure that their FCT testing is conducted according to industry standards and regulations, including proper calibration and maintenance of test systems, testing elements according to specifications, and documenting all test results and modifications made during the process.
Common Challenges and Considerations in FCT Testing
Functional Circuit Test (FCT) is an integral part of PCB manufacturing, but it comes with its own set of challenges. The complexity of modern PCB designs and the multitude of components and connections involved can make FCT testing difficult. Some of the common challenges include:
- Precise Temperature Control: FCT testing often requires specific temperature settings to simulate real-world operating conditions. Ensuring precise temperature control can be challenging but is crucial for accurate testing.
- Accurate Component Testing: FCT testing must accurately test each component on the PCB to ensure proper functionality. This requires advanced testing equipment and techniques to detect any faults or defects.
- Replicating Complex Connections: PCBs can have complex interconnections between components, which must be accurately replicated during testing. Ensuring that all connections are properly tested can be challenging.
- Time and Cost: FCT testing can be time-consuming and expensive, especially for large or complex PCBs. Manufacturers must find ways to optimize their testing processes to reduce time and cost.
To address these challenges, manufacturers can consider the following:
- Automated Testing: Investing in automated FCT systems can help streamline the testing process and reduce labor costs. Automated systems can perform tests quickly and accurately, saving time and effort.
- Outsourcing: Some companies choose to outsource their FCT testing needs to third-party providers. This can be cost-effective and ensures quality assurance for the device under test.
- System Evaluation: When selecting an FCT test system, it’s important to evaluate its performance, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with existing equipment. Additionally, ensure that the system meets safety standards and regulations.
By understanding these challenges and considerations, manufacturers can optimize their FCT testing processes and ensure the quality and reliability of PCB&PCBA.
Difference Between ICT and FCT in PCB Testing
In the realm of PCB testing, two primary methods stand out: In-Circuit Testing (ICT) and Functional Circuit Testing (FCT). While both are essential for ensuring PCB quality, they serve different purposes and are conducted at different stages of the manufacturing process.
In-Circuit Testing (ICT): ICT is a comprehensive method that focuses on testing individual elements on a PCB. It is particularly effective at identifying production defects such as open connections, faulty soldering, incorrect component placements, and incorrect component values. ICT is typically conducted using a bed-of-nails test system, where the PCB is connected to multiple points through spring contacts. This method provides detailed insights into the PCB’s physical properties and helps verify its structural integrity.
Functional Circuit Testing (FCT): On the other hand, FCT is geared towards assessing the overall functionality of a PCB. It involves stimulating the PCB with various voltages and currents to check its electrical characteristics. FCT is conducted after the PCB has been assembled to ensure that all components are working as intended, properly connected, and compliant with standards. This method helps identify and isolate defects that may affect the PCB’s performance in real-world applications.
While both ICT and FCT are crucial for PCB testing, they serve different purposes and provide different insights into the PCB’s quality. ICT focuses on individual elements and physical properties, while FCT assesses the overall functionality of the PCB. By combining these two testing methods, manufacturers can ensure that their PCBs meet high-quality standards and perform reliably in the field.
Conclusion
Functional Circuit Testing (FCT) plays a crucial role in ensuring the quality and reliability of printed circuit boards (PCBs) before they are released to the market. This testing process, conducted at the end of the production line, evaluates the board’s performance in its intended environment. FCT involves a combination of hardware and software components, including control units, test adapters, test applications, and sensors, to detect defects, vulnerabilities, and potential failures.
FCT tests vary in complexity, ranging from simple visual inspections to more intricate in-circuit tests that assess electrical inputs, user interface operations, and environmental conditions. By combining FCT with In-Circuit Testing (ICT), manufacturers can achieve higher accuracy in identifying faults such as incorrect component values, functional issues, and parametric issues.
Selecting the right test system is critical to ensuring quality results and optimizing production efficiency. It is also important for manufacturers to understand their responsibilities when conducting FCT, including proper calibration and maintenance of test systems, testing elements according to specifications, and documenting all test results and modifications made during the process.
At our company, we offer professional services for printed circuit board assemblies, including FCT testing, to help ensure that your PCBs meet the highest standards of quality and reliability. Contact us today to learn more about how we can support your PCB manufacturing needs.
PCB & PCBA quick quote
Related Articles

Understanding Aluminum Substrate PCB: Types and Advantages
[pac_divi_table_of_contents title="On this article" default_state="closed" included_headings="off|on|on|off|off|off" exclude_headings_by_class="on" active_link_highlight="on" level_markers_3="icons" title_container_padding="10px|15px|10px|15px|true|false"...

Characteristics and Applications of Black Core PCB Material
[pac_divi_table_of_contents title="On this article" default_state="closed" included_headings="off|on|on|off|off|off" exclude_headings_by_class="on" active_link_highlight="on" level_markers_3="icons" title_container_padding="10px|15px|10px|15px|true|false"...

Key Considerations for Special PCB Manufacturing
[pac_divi_table_of_contents title="On this article" default_state="closed" included_headings="off|on|on|off|off|off" exclude_headings_by_class="on" active_link_highlight="on" level_markers_3="icons" title_container_padding="10px|15px|10px|15px|true|false"...
Take a Quick Quote
